end tidal co2 range cpr
These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression generating reasonable pulmonary blood flow justifying continuation of resuscitation. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.

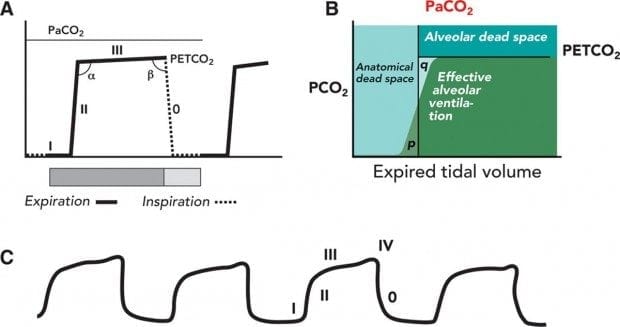
. PaCO2 PetCO2 End tidal measurement from expired or exhaled air PaCO2 Arterial blood gas sample End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. J Intensive Care Med. An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed.
However EtCO2 provides the same information an. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2 therefore monitoring of ETCO2 provides very useful information to guide treatment during CPR 8 - 10. Attach the in-line connector to the breathing circuit ensuring that a bacterialviral filter is connected to the airway adjunct maskLMAETT.
428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. N Engl J Med.
Chest compression provider tiring end-tidal CO2 value diminishes over time. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST. Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2.
Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective. I can look at those numbers and adjust my ventilator accordingly to keep them within a normal range. Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists.
4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. To identify whether any level of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 measured during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR correlates with return of spontaneous circulation ROSC or survival in adults experiencing cardiac arrest in any setting.
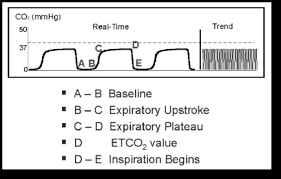
The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns. Quality of CPR.
However in ACLS and in a cardiac arrest Im using end-tidal not necessarily for the pulmonary or respiratory status but to look at the function of the pump the function of the heart. Literature search was performed using Medline and EMBASE. The height of the ETCO2 waveform during CPR has been used as an indirect measure of adequate chest compressions helping those involved in resuscitation monitor the effectiveness of their compressions in real time.
Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector. High quality CPR consistent waveform and end-tidal CO2 20 kPa. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al.
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. Which will leave them at the higher end of this range eg a pH of 74. EtCO2 reveals the amount of CO2 being cleared from the body which is a reflection of the quality of CPR as well as the bodys CO2 production.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest. Remove the corpuls3 disposable CO2 oral connector from its package.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Patients with lung disease and a larger etCO2-PaCO2 gap may have a somewhat higher PaCO2 and a thus a. Quantitative End-tidal CO2 has quickly become the standard of care for monitoring the efficiency of CPR.
The height of the capnography waveform accompanies this number on the monitor as well as the. Connect the capONE sensors x2 to the CO2 oral connector. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC.
10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC.
We typically assess quality of CPR by palpable pulses but this can be challenging and even unreliable. Remember a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45. Confirm appropriate CO2 values are displayed.
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR adequate chest compressions generate a cardiac output of 17 to 27 allowing CO 2 circulation for exhalation. 10 to 20 mmHg during CPR was strongly associated with ROSC while persistent EtCO2 below 10 to 20 mmHg after 20 minutes of CPR had a 05 likelihood of ROSC. In the field monitoring ETco 2 during endotracheal-tube placement can verify correct tube placement and indicate tube dislodgement during transport.
In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. We included randomized controlled trials cohort studies and case-control studies of adult cardiac.
The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to explore whether ETCO2 values could be utilised as a tool to predict the outcome of resuscitation. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check. In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was.
Arterial diastolic pressure 25 mm Hg may be useful but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. By monitoring the CO2 coming from the lungs we can not only confirm placement of an endotracheal tube after intubation but using new technology with real-time electronic monitoring we can determine the levels of CO2 with each breath. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR ETCO2 concentration is a reliable index of effective heart compression during CPR which is associated with cardiac output 7 8.
EtCO2 is essentially to ensuring quality CPR. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Wayne MA Miller CC.
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Co2 Emergency Nursing Icu Nurse Critical Care Emergency Medical Technician

Making Waves The Use Of Waveform Capnography For Procedural Sedation In The Cardiac Cath Lab Nurse Anesthesia Cath Lab Nursing Emergency Medicine

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

What S In A Wave Form Utilizing End Tidal Capnography For More Than Intubation Confirmation Criticalcarenow

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Capnograph Note Try To Maintain Etco2 Above 10mmhg During Cpr Emergency Nursing Respiratory Therapy Student Icu Nursing